Makerville
Undergraduate Thesis
An approach towards active Maker Ecosystems in an Urban Environment

View Other Projects
A united and coordinated effort is necessary to rethink the way, location, and nature of our production, if we intend to live in harmony while respecting the limits of our planet’s resources. The suggested approach involves developing resilient, self-sufficient neighbourhoods and cities that can effectively tackle contemporary challenges. This entails regaining the expertise and capability to create products, generate energy, cultivate food, comprehend material flows, and empower citizens to take control of their own destinies.
This presents an occasion to construct cities anew, aligning philosophies, visions, and goals in tandem with existing innovation ecosystems. These ecosystems encompass decentralized innovation hubs such as Fab Labs, Makerspaces, and open communities, which have nurtured a knowledge-centred economy over the past decade. This economy revolves around open-source innovations, digital fabrication technologies, and distributed digital networks. The overarching objective is to curate a global repository of methodologies detailing how items are produced, their constituents, and the underlying rationales.
Takeaway & Reflection









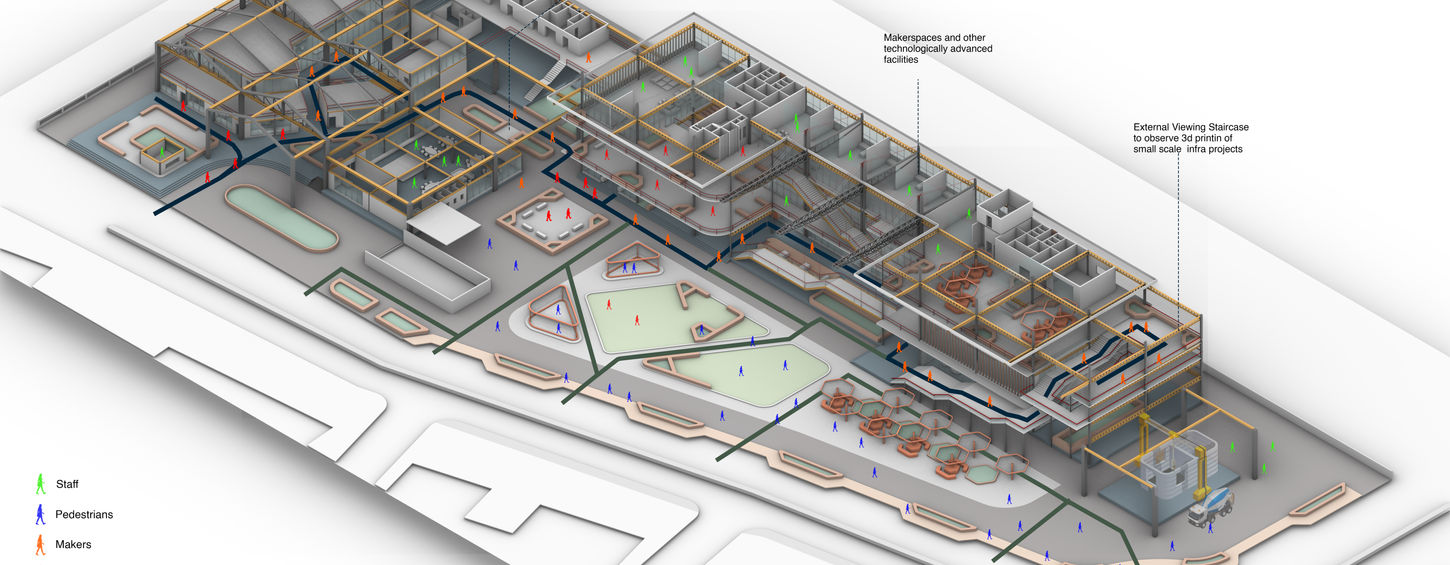
F.13 - Architectural Details
F.13 - Architectural Sections
F.13 - Architectural Plans
F.13 - Design Development
F.11 Design Strategies & Goals

F.11 - Program Development
F.10 Design Objectives

E. Site Analysis
D. Case Studies
C. The Way Forward - Development of Business Model
The survey information offers some insight regarding the maker’s profile that calls for further inquiry.
1. Affordability poses a challenge for many to participate. An economic business model to counter this is to be thought of.
2. The elderly have a willingness to participate along with the necessary aid.
3. People with tertiary education should also be encouraged to engage in making by providing necessary technical guidance and support.
4. Unemployed and economically disadvantaged citizens to be empowered with necessary training and skill development.
5. Fab labs or maker labs attached to institutes have restricted entry and time constraints.
Inference B
B.4b - Surveys & Interviews
B.4a & 4b - Statistics of Makerspaces, Identification of Problems


B.3b - Strategies for Circular Economy

B.3a - Fab City Global Manifesto
The existing module of a Makerspace in the 4th IR has already established that Human capital is indispensable. Taking this into account enhancement of the present, the module that aligns adapts and responds to the goal of INNOVATION + PURPOSE + INCLUSIVITY is needed, which can open the way to curiosity, empathy and judgement ensuring balance between people and technology.
Inference A
A.2c - Advantages, Need & Significance


A.2b - The Process
A.2a - Elements & Components of a Makerspace


A.1b - The Maker Movement

A.1a - Timeline of Industrial Revolution

Research Methodology
Details
My Role
Undergraduate Student at Academy of Architecture, Mumbai
Location
Mumbai, India
Thesis Advisor
Ar. Prof. Mythili Kowshik Shetty
Project Outline
Primarily, to study, analyze and enhance the business model of a Makerspace to generate adequate revenue, and become a source of livelihood, education and innovation while being centric on localized production and circular economic development. Secondarily, to propose a network of makerspaces at a city level and demonstrate the function by means of a prototypical architectural intervention that satisfies social, economic and infrastructural needs as a step towards self-sufficient neighbourhoods and cities.